Using Blender for Scientific Visualization
Result:
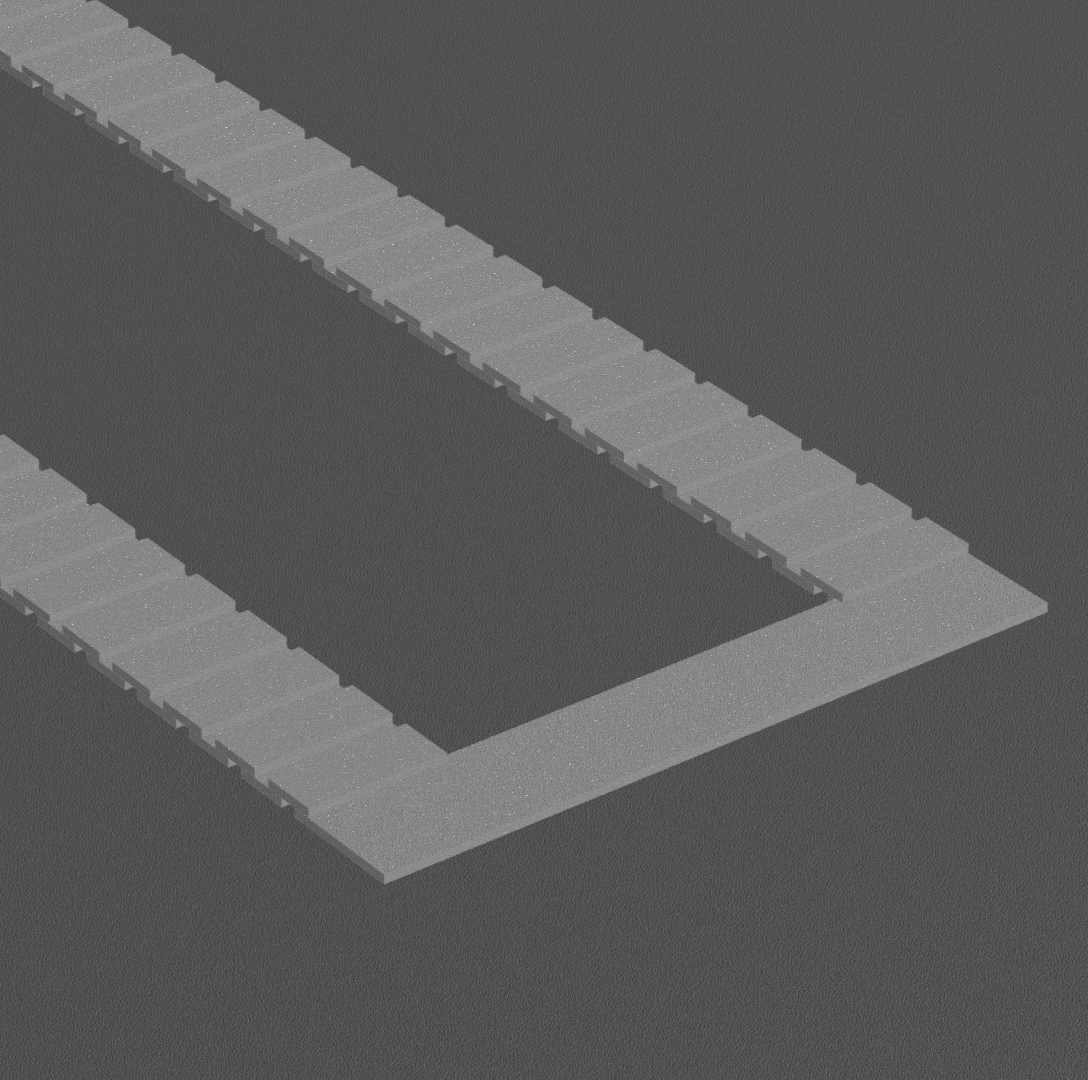 Script (Blender 3.6 LTS):
Script (Blender 3.6 LTS):
import bpy
import math
from mathutils import Vector
###############################
# Step 1: Clean up all objects
###############################
bpy.ops.object.select_all(action='SELECT')
bpy.ops.object.delete(use_global=False)
###########################
# Step 2: Main code (Josephson chain setup)
###########################
# Parameters for the unit cell
unit_length = 1.0 # Adjust the size as needed
length_ratio = 15
width_ratio = 6
height_ratio = 1
num_cells = 50 # Number of unit cells to duplicate in each layer
y_interval = 4 # Spacing between each unit cell along the Y-axis
layer_offset_y = 2 # Offset for the second layer in the Y-axis
x_offset = 30 # Spacing between each duplicated chain along the X-axis
num_chains = 2 # Number of chains to duplicate along the X-axis
# Calculate dimensions
unit_cell_length = unit_length * length_ratio
unit_cell_width = unit_length * width_ratio
unit_cell_height = unit_length * height_ratio
# Create a single unit cell as the basis
bpy.ops.mesh.primitive_cube_add(size=1)
unit_cell = bpy.context.object
unit_cell.scale = (unit_cell_length / 2, unit_cell_width / 2, unit_cell_height / 2)
unit_cell.location = (0, 0, unit_cell_height / 2)
unit_cell.name = "Unit_Cell"
def create_chain(x_location):
first_layer = []
for i in range(num_cells):
new_cell = unit_cell.copy()
new_cell.data = unit_cell.data.copy()
new_cell.location = (x_location, i * y_interval, unit_cell_height / 2)
bpy.context.collection.objects.link(new_cell)
first_layer.append(new_cell)
# Second layer
for cell in first_layer:
new_cell = cell.copy()
new_cell.data = cell.data.copy()
new_cell.location = (
cell.location[0],
cell.location[1] + layer_offset_y,
cell.location[2] + unit_cell_height / 2
)
bpy.context.collection.objects.link(new_cell)
# Create multiple chains
for j in range(num_chains):
create_chain(x_location=j * x_offset)
# Create a large background plane
bpy.ops.mesh.primitive_plane_add(size=500)
background_plane = bpy.context.object
background_plane.location = (0, 0, 0)
background_plane.rotation_euler = (0, 0, 0)
background_plane.name = "Background_Plane"
# Metallic material functions
def create_realistic_metallic_material(name, base_color, bump_strength=0.1, noise_scale=50.0):
mat = bpy.data.materials.new(name=name)
mat.use_nodes = True
nodes = mat.node_tree.nodes
links = mat.node_tree.links
principled = nodes.get("Principled BSDF")
principled.inputs["Base Color"].default_value = base_color
principled.inputs["Metallic"].default_value = 0.5
principled.inputs["Roughness"].default_value = 0.3
noise = nodes.new(type="ShaderNodeTexNoise")
noise.inputs["Scale"].default_value = noise_scale
noise.inputs["Detail"].default_value = 10.0
noise.inputs["Roughness"].default_value = 0.5
bump = nodes.new(type="ShaderNodeBump")
bump.inputs["Strength"].default_value = bump_strength
ramp = nodes.new(type="ShaderNodeValToRGB")
ramp.color_ramp.interpolation = 'LINEAR'
ramp.color_ramp.elements[0].position = 0.4
ramp.color_ramp.elements[1].position = 0.6
links.new(noise.outputs["Fac"], ramp.inputs["Fac"])
links.new(ramp.outputs["Color"], principled.inputs["Roughness"])
links.new(noise.outputs["Fac"], bump.inputs["Height"])
links.new(bump.outputs["Normal"], principled.inputs["Normal"])
return mat
realistic_metal = create_realistic_metallic_material(
"Realistic_Microchip_Metal", (0.4, 0.4, 0.4, 1), bump_strength=1.3, noise_scale=500.0
)
for obj in bpy.context.collection.objects:
if "Unit_Cell" in obj.name:
obj.data.materials.clear()
obj.data.materials.append(realistic_metal)
background_color = (0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 1)
background_mat = create_realistic_metallic_material(
"Background_Material", background_color, bump_strength=0.6, noise_scale=10000.0
)
background_plane.data.materials.clear()
background_plane.data.materials.append(background_mat)
# Add a connector block
bpy.ops.mesh.primitive_cube_add(size=1)
connector = bpy.context.object
connector.scale = (x_offset+unit_cell_length/2, unit_cell_width*2/2, unit_cell_height/2)
connector.location = ((num_chains - 1) * x_offset/2, -y_interval/2, unit_cell_height / 2)
connector.name = "Connector"
connector.data.materials.clear()
connector.data.materials.append(realistic_metal)
print("C-shaped connector added.")
# Env lighting
bpy.context.scene.world.use_nodes = True
wnodes = bpy.context.scene.world.node_tree.nodes
for node in wnodes:
wnodes.remove(node)
bg = wnodes.new(type="ShaderNodeBackground")
bg.inputs["Color"].default_value = (0.3, 0.3, 0.3, 1)
bg.inputs["Strength"].default_value = 0.3
out = wnodes.new(type="ShaderNodeOutputWorld")
bpy.context.scene.world.node_tree.links.new(bg.outputs["Background"], out.inputs["Surface"])
# Sun lamp
bpy.ops.object.light_add(type='SUN', align='WORLD', location=(10, -10, 20))
sun = bpy.context.object
sun.data.energy = 5.0
sun.rotation_euler = (0.785, 0.785, 0)
sun.data.shadow_soft_size = 0.5
sun.data.use_shadow = True
######################
# Step 3: Camera + Animation
######################
bpy.ops.object.camera_add(location=(0,0,0))
camera = bpy.context.object
camera.name = "Main_Camera"
bpy.context.scene.camera = camera
# Set camera properties for better framing
camera.data.lens = 50 # 50mm focal length for a natural perspective
camera.data.dof.use_dof = True
camera.data.dof.focus_distance = 40.0 # Approximate distance to target
fps = 12
duration_seconds = 10
frame_count = fps * duration_seconds
bpy.context.scene.frame_start = 1
bpy.context.scene.frame_end = frame_count
# Target point that camera will always face
target_x = 15
target_y = 50.0
target_z = 0.0
target = Vector((target_x, target_y, target_z))
radius = 40.0
height = 20.0
for frame in range(1, frame_count + 1):
bpy.context.scene.frame_set(frame)
t = (frame - 1) / (frame_count - 1) # fraction from 0..1
angle = 2.0 * math.pi * t # revolve 0..360
# Calculate camera position
x = target_x + radius * math.cos(angle)
y = target_y + radius * math.sin(angle)
z = target_z + height
camera.location = (x, y, z)
# Point camera at target
direction = target - Vector(camera.location)
rot_quat = direction.to_track_quat('-Z', 'Y')
camera.rotation_mode = 'QUATERNION'
camera.rotation_quaternion = rot_quat
# Insert keyframes
camera.keyframe_insert(data_path='location')
camera.keyframe_insert(data_path='rotation_quaternion')
# Add an Empty at target point for visualization (helpful during setup)
bpy.ops.object.empty_add(type='PLAIN_AXES', location=(target_x, target_y, target_z))
target_empty = bpy.context.object
target_empty.name = "Camera_Target"
target_empty.scale = (2, 2, 2) # Make it easier to see
################
# Step 4: Output
################
bpy.context.scene.render.filepath = "/Users/jiakai/Desktop/josephson_frames/"
bpy.context.scene.render.image_settings.file_format = 'PNG'
print("Setup complete. Render with 'Render → Render Animation' or:")
bpy.ops.render.render('INVOKE_DEFAULT', animation=True)