Using Blender for Scientific Visualization
Result:
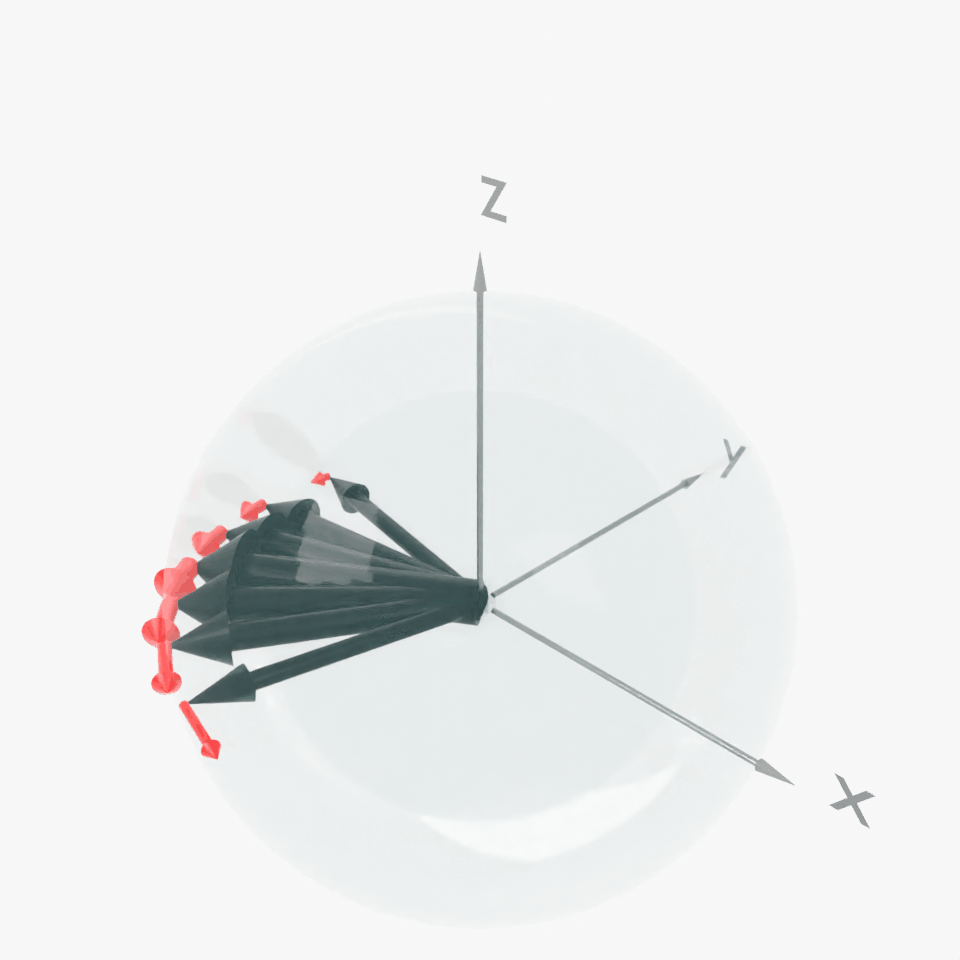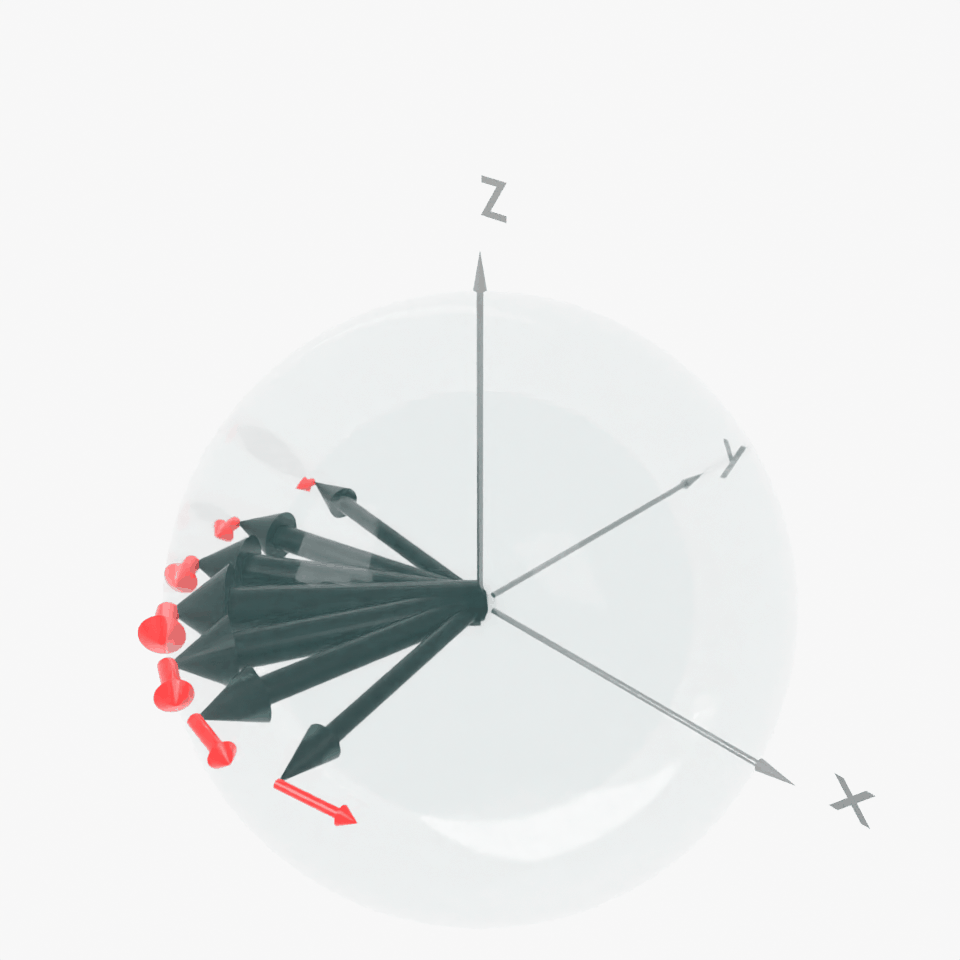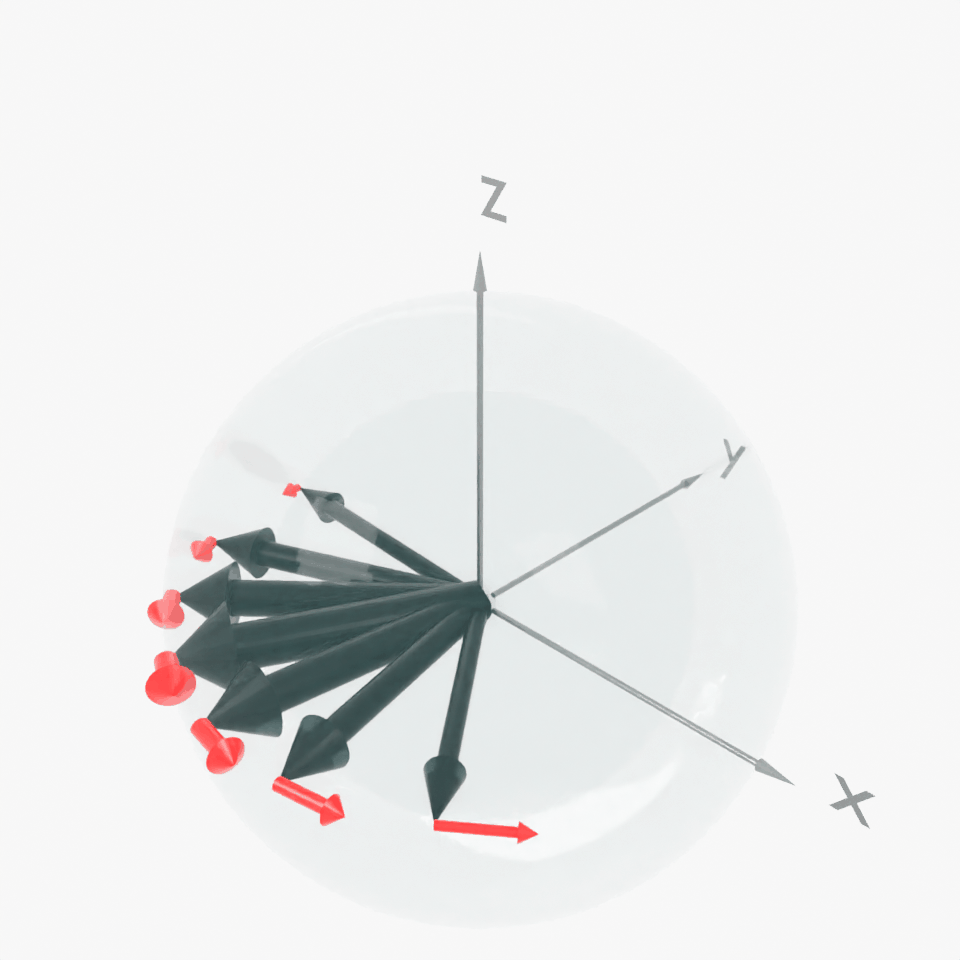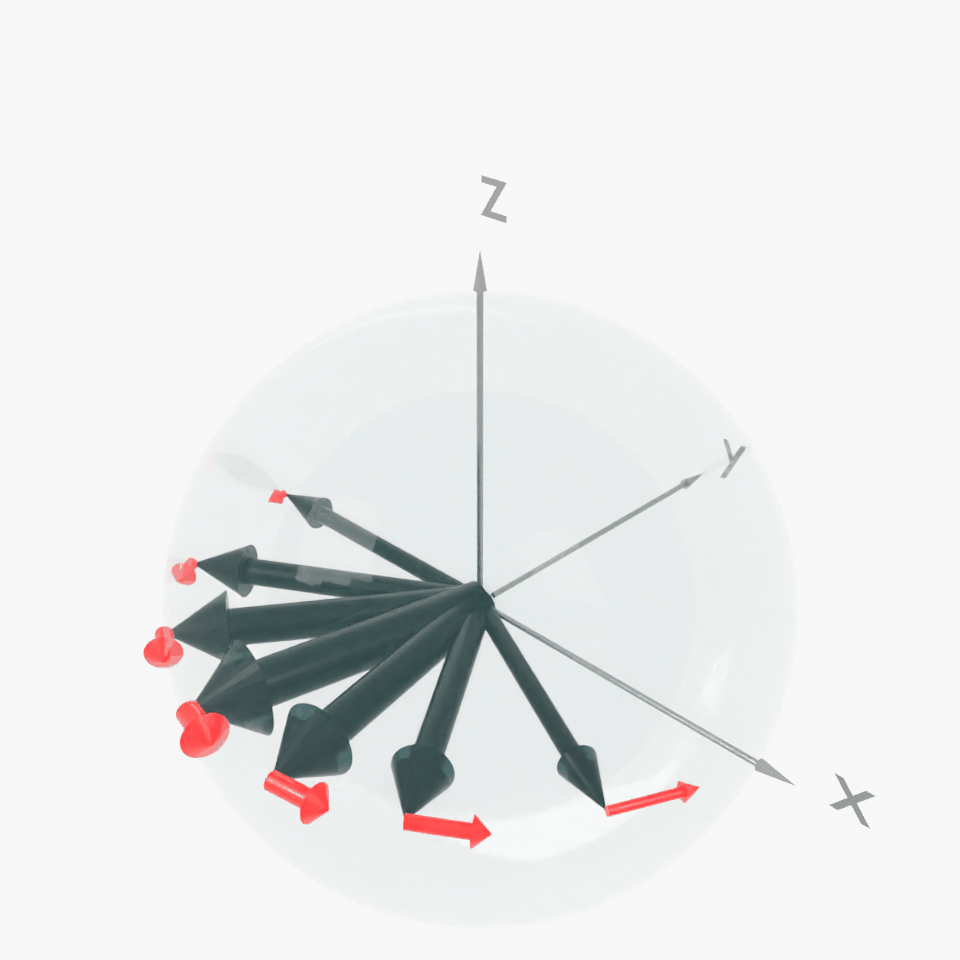
Result:
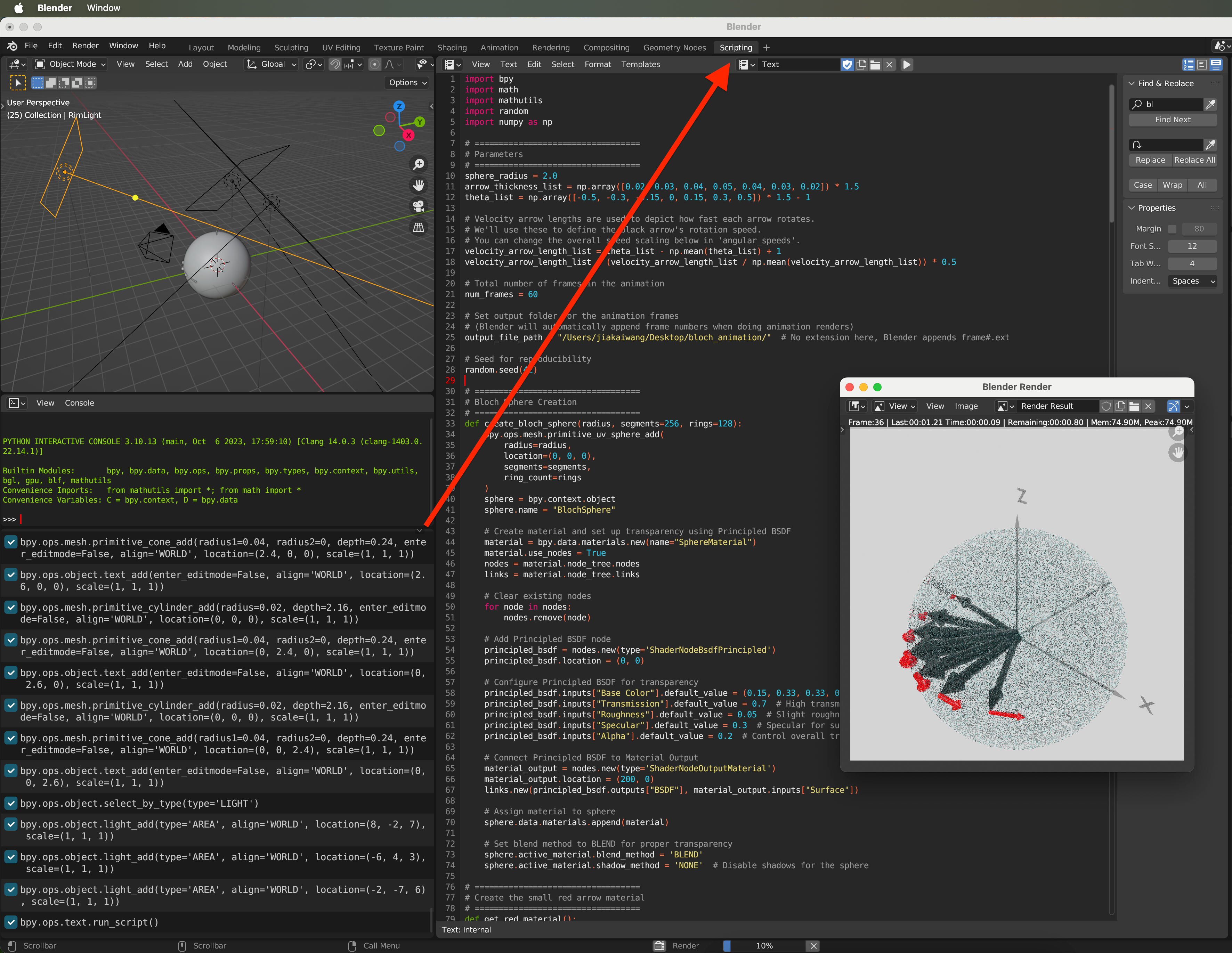
Script (Blender 3.6 LTS):
import bpy
import math
import mathutils
import random
import numpy as np
# ==================================
# Parameters
# ==================================
sphere_radius = 2.0
arrow_thickness_list = np.array([0.02, 0.03, 0.04, 0.05, 0.04, 0.03, 0.02]) * 1.5
theta_list = np.array([-0.5, -0.3, -0.15, 0, 0.15, 0.3, 0.5]) * 1.5 - 1
# Velocity arrow lengths are used to depict how fast each arrow rotates.
# We'll use these to define the black arrow's rotation speed.
# You can change the overall speed scaling below in 'angular_speeds'.
velocity_arrow_length_list = theta_list - np.mean(theta_list) + 1
velocity_arrow_length_list = (velocity_arrow_length_list / np.mean(velocity_arrow_length_list)) * 0.5
# Total number of frames in the animation
num_frames = 60
# Set output folder for the animation frames
# (Blender will automatically append frame numbers when doing animation renders)
output_file_path = "/Users/jiakaiwang/Desktop/bloch_animation/" # No extension here, Blender appends frame#.ext
# Seed for reproducibility
random.seed(42)
# ==================================
# Bloch Sphere Creation
# ==================================
def create_bloch_sphere(radius, segments=256, rings=128):
bpy.ops.mesh.primitive_uv_sphere_add(
radius=radius,
location=(0, 0, 0),
segments=segments,
ring_count=rings
)
sphere = bpy.context.object
sphere.name = "BlochSphere"
# Create material and set up transparency using Principled BSDF
material = bpy.data.materials.new(name="SphereMaterial")
material.use_nodes = True
nodes = material.node_tree.nodes
links = material.node_tree.links
# Clear existing nodes
for node in nodes:
nodes.remove(node)
# Add Principled BSDF node
principled_bsdf = nodes.new(type='ShaderNodeBsdfPrincipled')
principled_bsdf.location = (0, 0)
# Configure Principled BSDF for transparency
principled_bsdf.inputs["Base Color"].default_value = (0.15, 0.33, 0.33, 0.4) # Slight grey color
principled_bsdf.inputs["Transmission"].default_value = 0.7 # High transmission for transparency
principled_bsdf.inputs["Roughness"].default_value = 0.05 # Slight roughness
principled_bsdf.inputs["Specular"].default_value = 0.3 # Specular for subtle highlights
principled_bsdf.inputs["Alpha"].default_value = 0.2 # Control overall transparency
# Connect Principled BSDF to Material Output
material_output = nodes.new(type='ShaderNodeOutputMaterial')
material_output.location = (200, 0)
links.new(principled_bsdf.outputs["BSDF"], material_output.inputs["Surface"])
# Assign material to sphere
sphere.data.materials.append(material)
# Set blend method to BLEND for proper transparency
sphere.active_material.blend_method = 'BLEND'
sphere.active_material.shadow_method = 'NONE' # Disable shadows for the sphere
# ==================================
# Create the small red arrow material
# ==================================
def get_red_material():
red_material = bpy.data.materials.new(name="RedMaterial")
red_material.use_nodes = True
bsdf_red = red_material.node_tree.nodes.get("Principled BSDF")
if bsdf_red:
bsdf_red.inputs["Base Color"].default_value = (1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0) # Pure red
bsdf_red.inputs["Roughness"].default_value = 0.3
bsdf_red.inputs["Specular"].default_value = 0.5
return red_material
# ==================================
# Arrow Creation
# ==================================
def create_arrow(name, arrow_thickness, red_material, red_speed):
"""
Creates a black arrow (shaft + tip) along local +Z from 0..1 in local space.
Then creates a smaller red arrow along local +X from 0..1 in local space,
and offsets it so that its base is at local z=1.
That way, the red arrow is perpendicular (tangent) to the black arrow tip.
"""
# Create an empty that we will parent the arrow objects to, so we can rotate it easily.
empty = bpy.data.objects.new(f"{name}_Empty", None)
bpy.context.scene.collection.objects.link(empty)
# Hide or shrink empty
empty.empty_display_type = 'PLAIN_AXES'
empty.empty_display_size = 0.0001
# ================= Black Arrow (Shaft + Tip) =================
# 1) Shaft: from z=0 to z=0.8 (0.8 long)
bpy.ops.mesh.primitive_cylinder_add(radius=arrow_thickness, depth=0.8, location=(0, 0, 0.4))
arrow_shaft = bpy.context.object
arrow_shaft.name = f"{name}_Shaft"
arrow_shaft.parent = empty
# 2) Tip: from z=0.8 to z=1.0 (0.2 long)
bpy.ops.mesh.primitive_cone_add(
radius1=arrow_thickness * 2,
radius2=0.0,
depth=0.2,
location=(0, 0, 0.9) # center at 0.9 so half extends up to 1.0
)
arrow_tip = bpy.context.object
arrow_tip.name = f"{name}_Tip"
# Create a black material
arrow_material = bpy.data.materials.new(name=f"{name}Material")
arrow_material.use_nodes = True
bsdf = arrow_material.node_tree.nodes.get("Principled BSDF")
if bsdf:
bsdf.inputs["Base Color"].default_value = (0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0)
bsdf.inputs["Roughness"].default_value = 0.3
bsdf.inputs["Specular"].default_value = 0.1
arrow_shaft.data.materials.append(arrow_material)
arrow_tip.data.materials.append(arrow_material)
arrow_shaft.active_material.blend_method = 'OPAQUE'
arrow_shaft.active_material.shadow_method = 'NONE'
arrow_tip.active_material.blend_method = 'OPAQUE'
arrow_tip.active_material.shadow_method = 'NONE'
# Parent them under the empty
arrow_shaft.parent = empty
arrow_tip.parent = empty
# ================= Red Arrow (Shaft + Tip) =================
# We'll define it along local +X from x=0..1.
# Then place it so that x=0 is at local z=1.
red_shaft_length = 5 * red_speed # pick your formula
bpy.ops.mesh.primitive_cylinder_add(
radius=arrow_thickness * 0.5,
depth=red_shaft_length,
location=(red_shaft_length / 2, 0, 0)
)
small_shaft = bpy.context.object
small_shaft.name = f"{name}_Small_Shaft"
# Rotate so it extends along local X. By default, a cylinder extends local Z, so rotate -90 around Y.
small_shaft.rotation_euler = (0, math.radians(90), 0)
# 2) Red tip: length=0.1. place at x=0.4..0.5? We'll do location=0.45 for center.
red_tip_length = max(0.05, 0.25 * red_shaft_length) # optional scaling for the tip
bpy.ops.mesh.primitive_cone_add(
radius1=arrow_thickness,
radius2=0.0,
depth=red_tip_length,
location=(red_shaft_length + red_tip_length/2, 0, 0)
)
small_tip = bpy.context.object
small_tip.name = f"{name}_Small_Tip"
small_tip.rotation_euler = (0, math.radians(90), 0)
# Assign red material
small_shaft.data.materials.append(red_material)
small_tip.data.materials.append(red_material)
small_shaft.active_material.blend_method = 'OPAQUE'
small_shaft.active_material.shadow_method = 'NONE'
small_tip.active_material.blend_method = 'OPAQUE'
small_tip.active_material.shadow_method = 'NONE'
# Create an empty for the red arrow so we can shift it to z=1 in local coords
red_empty = bpy.data.objects.new(f"{name}_Red_Empty", None)
bpy.context.scene.collection.objects.link(red_empty)
red_empty.empty_display_type = 'PLAIN_AXES'
red_empty.empty_display_size = 0.0001
red_empty.parent = empty
red_empty.location = (0, 0, 1.0) # place it at black arrow tip in local coords
# Parent the red shaft & tip to red_empty
small_shaft.parent = red_empty
small_tip.parent = red_empty
return empty, arrow_shaft, arrow_tip, small_shaft, small_tip
# ==================================
# Add Lighting
# ==================================
def add_lighting():
# Remove existing lights
bpy.ops.object.select_by_type(type='LIGHT')
bpy.ops.object.delete()
# Add a key light - main illumination
bpy.ops.object.light_add(type='AREA', location=(8, -2, 7))
key_light = bpy.context.object
key_light.name = "KeyLight"
key_light.data.energy = 800
key_light.data.size = 5
key_light.rotation_euler = (math.radians(-45), math.radians(15), 0)
# Add a fill light
bpy.ops.object.light_add(type='AREA', location=(-6, 4, 3))
fill_light = bpy.context.object
fill_light.name = "FillLight"
fill_light.data.energy = 400
fill_light.data.size = 7
fill_light.rotation_euler = (math.radians(30), math.radians(-20), 0)
# Add a rim light
bpy.ops.object.light_add(type='AREA', location=(-2, -7, 6))
rim_light = bpy.context.object
rim_light.name = "RimLight"
rim_light.data.energy = 600
rim_light.data.size = 4
rim_light.rotation_euler = (math.radians(60), math.radians(-30), 0)
# ==================================
# Create coordinate axis arrow
# ==================================
def create_axis_arrow(start, end, color, name):
direction = mathutils.Vector(end) - mathutils.Vector(start)
length = direction.length
direction.normalize()
# Create cylinder for the arrow shaft
bpy.ops.mesh.primitive_cylinder_add(
radius=0.02,
depth=length * 0.9,
location=(0, 0, 0)
)
arrow_shaft = bpy.context.object
arrow_shaft.name = f"{name}_Shaft"
# Position/rotate the arrow shaft
mid_point_shaft = (mathutils.Vector(start) + mathutils.Vector(end)) / 2
arrow_shaft.location = mid_point_shaft
arrow_shaft.rotation_mode = 'QUATERNION'
arrow_shaft.rotation_quaternion = direction.to_track_quat('Z', 'Y')
# Create the cone for the arrow tip
cone_length = length * 0.1
bpy.ops.mesh.primitive_cone_add(
radius1=0.04,
radius2=0.0,
depth=cone_length,
location=end
)
arrow_tip = bpy.context.object
arrow_tip.name = f"{name}_Tip"
# Reposition and rotate the tip
arrow_tip.rotation_mode = 'QUATERNION'
arrow_tip.rotation_quaternion = direction.to_track_quat('Z', 'Y')
tip_offset = mathutils.Vector((0, 0, -cone_length / 2))
tip_offset.rotate(arrow_tip.rotation_quaternion)
arrow_tip.location = mathutils.Vector(end) + tip_offset
# Create and apply colored material
axis_material = bpy.data.materials.new(name=f"{name}Material")
axis_material.use_nodes = True
bsdf = axis_material.node_tree.nodes.get("Principled BSDF")
if bsdf:
bsdf.inputs["Base Color"].default_value = (*color, 1.0)
bsdf.inputs["Metallic"].default_value = 0.8
bsdf.inputs["Roughness"].default_value = 0.2
arrow_shaft.data.materials.append(axis_material)
arrow_tip.data.materials.append(axis_material)
return arrow_shaft, arrow_tip
# ==================================
# Create text label
# ==================================
def create_text_label(text, location, size=0.2):
bpy.ops.object.text_add(location=location)
text_obj = bpy.context.object
text_obj.data.body = text
text_obj.data.size = size
# Create material for text
text_material = bpy.data.materials.new(name=f"Text_{text}_Material")
text_material.use_nodes = True
bsdf = text_material.node_tree.nodes.get("Principled BSDF")
if bsdf:
bsdf.inputs["Base Color"].default_value = (0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 1.0)
bsdf.inputs["Metallic"].default_value = 0.0
bsdf.inputs["Roughness"].default_value = 0.5
text_obj.data.materials.append(text_material)
# Rotate text to face camera (Z up in Blender, so rotate 90 deg around X)
text_obj.rotation_euler = (math.radians(90), 0, 0)
return text_obj
# ==================================
# MAIN SCRIPT
# ==================================
# --- Cleanup (optional) ---
bpy.ops.object.select_all(action='SELECT')
bpy.ops.object.delete(use_global=False)
# Create Bloch sphere
create_bloch_sphere(sphere_radius)
# Create red material for small arrows
red_material = get_red_material()
# Create black arrows with small red arrows. We'll store references for animation.
arrows = []
# We'll define a separate angular speed for each arrow.
# The velocity_arrow_length_list can represent how quickly each arrow rotates in the XY-plane.
angular_speeds = velocity_arrow_length_list * 0.05 # scale factor for rotation speed
for i, (theta, arrow_thickness, speed) in enumerate(zip(theta_list, arrow_thickness_list, angular_speeds)):
name = f"Arrow_{i}"
empty_obj, arrow_shaft, arrow_tip, small_shaft, small_tip = create_arrow(
name, arrow_thickness, red_material, speed # pass speed here
)
# Move the empty to the origin, but orient it so arrow lies on XY-plane initially at angle 'theta'.
# We'll define the arrow base at the origin, so we rotate around Z.
# Then we move it outward so arrow tip is on the Bloch sphere surface.
# We'll store a custom property for each arrow: initial angle and rotation speed.
empty_obj["initial_theta"] = theta
empty_obj["angular_speed"] = speed
# We'll place the arrow so that it extends from the origin.
# The arrow local transform is from z=0..1. We'll rotate around X 90 deg to make it point outward in XY-plane, then around Z by 'theta'.
empty_obj.rotation_euler = (math.radians(90), 0, theta)
# We'll do uniform scale so the arrow length is sphere_radius.
empty_obj.scale = (sphere_radius, sphere_radius, sphere_radius)
arrows.append(empty_obj)
# Create coordinate axes and labels
axis_length = sphere_radius * 1.2
x_arrow = create_axis_arrow((0, 0, 0), (axis_length, 0, 0), (0.2, 0.2, 0.2), "X_Axis")
x_label = create_text_label("x", (axis_length + 0.2, 0, 0), size=0.5)
y_arrow = create_axis_arrow((0, 0, 0), (0, axis_length, 0), (0.2, 0.2, 0.2), "Y_Axis")
y_label = create_text_label("y", (0, axis_length + 0.2, 0), size=0.5)
z_arrow = create_axis_arrow((0, 0, 0), (0, 0, axis_length), (0.2, 0.2, 0.2), "Z_Axis")
z_label = create_text_label("z", (0, 0, axis_length + 0.2), size=0.5)
# Add lighting
add_lighting()
# Create a camera
camera_data = bpy.data.cameras.new("Camera")
camera_object = bpy.data.objects.new("Camera", camera_data)
bpy.context.scene.collection.objects.link(camera_object)
bpy.context.scene.camera = camera_object
# Position the camera
camera_object.location = (5, -5, 5)
camera_object.rotation_euler = (math.radians(60), 0, math.radians(45))
# Cycles render settings
bpy.context.scene.render.engine = 'CYCLES'
bpy.context.scene.cycles.samples = 10
bpy.context.scene.cycles.max_bounces = 12
bpy.context.scene.cycles.caustics_reflective = False
bpy.context.scene.cycles.caustics_refractive = False
bpy.context.scene.cycles.transparent_min_bounces = 8
bpy.context.scene.cycles.transparent_max_bounces = 32
# Resolution
bpy.context.scene.render.resolution_x = 960 # half width
bpy.context.scene.render.resolution_y = 960 # half height
bpy.context.scene.render.resolution_percentage = 100
# File path for animation (no extension, so Blender appends frame numbers)
bpy.context.scene.render.filepath = output_file_path
# World settings for white background
bpy.context.scene.world.use_nodes = True
world_nodes = bpy.context.scene.world.node_tree.nodes
for node in world_nodes:
world_nodes.remove(node)
bg_node = world_nodes.new(type='ShaderNodeBackground')
bg_node.inputs['Color'].default_value = (1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0)
bg_node.inputs['Strength'].default_value = 1.0
world_output = world_nodes.new(type='ShaderNodeOutputWorld')
world_output.location = (200, 0)
links = bpy.context.scene.world.node_tree.links
links.new(bg_node.outputs['Background'], world_output.inputs['Surface'])
# ==================================
# Create Keyframes for Animation
# ==================================
# We'll set the scene frame range
bpy.context.scene.frame_start = 0
bpy.context.scene.frame_end = num_frames
# For each frame, we'll position/rotate each arrow according to angular_speed.
# The arrow's angle(t) = initial_theta + angular_speed * t * 2pi (for full rotations).
for frame in range(num_frames + 1):
bpy.context.scene.frame_set(frame)
# time factor (assuming 24 fps)
t = frame / 12.0
for empty_obj in arrows:
init_theta = empty_obj["initial_theta"]
speed = empty_obj["angular_speed"]
angle = init_theta + speed * t * 2.0 * math.pi
# Keep X=90 deg, Y=0, Z=angle
empty_obj.rotation_euler = (math.radians(90), 0, angle)
empty_obj.keyframe_insert(data_path="rotation_euler")
print("Animation keyframes set. You can now render the animation.")
bpy.ops.render.render('INVOKE_DEFAULT', animation=True)
Finally convert image to gif with some preprocessing:
from PIL import Image, ImageEnhance
import os
# Assuming all images are in the same folder and named sequentially
image_folder = "./"
image_files = sorted([f for f in os.listdir(image_folder) if f.endswith('.png')]) # or .jpg
brightness_factor = 1.2 # >1 = brighter, <1 = darker
# Collect and sort image filenames
image_files = sorted(f for f in os.listdir(image_folder) if f.endswith('.png'))
# Load and brighten images
bright_images = []
for fname in image_files:
img_path = os.path.join(image_folder, fname)
img = Image.open(img_path).convert("RGB") # Convert to RGB to avoid palette issues
enhancer = ImageEnhance.Brightness(img)
bright_img = enhancer.enhance(brightness_factor)
bright_images.append(bright_img)
# Save as animated GIF
bright_images[0].save("output.gif",
save_all=True,
append_images=bright_images[1:],
duration=41.66, # 24fps = 41.66ms per frame
loop=0)